Page 95 - 《精细化工》2022年第6期
P. 95
第 6 期 赵梦阳,等: 导热增强聚氨酯基柔性定形相变材料的制备及性能 ·1161·
由图 11a 可以看到 , 在不同温 度 下 , PU/ CNTs 为功能性材料,通过一锅法制备了导热增强聚
APDMS-1/CNTs 的表面温度最高分别为 37.6、42.8、 氨酯基柔性定形相变材料。其中,PU/APDMS-1/
52.0、60.1、69.8 ℃,该材料将芯片表面温度降低了 CNTs 的相变焓值为 88.3 J/g,具有良好的热稳定性
2.4、7.2、8.0、9.9、10.2 ℃,有效地将芯片表面温 和定形效果。APDMS 的加入明显改善了相变材料
度更快地传递到外界环境中,降低了芯片表面工作 的柔性性能,该材料可以很好地弯曲旋转。均匀掺
温度,减小了芯片因工作温度过高而损坏的风险。 杂的 CNTs 使 PU/APDMS-1/CNTs 能够实现光热转
同时由图 11b 可以看到,在散热片 55 ℃下, 换和热能存储,其光热转换和热能存储效率为
PU/APDMS-1/CNTs 可以很好地贴合散热片进行弯 62.8%,与未加入 CNTs 的柔性相变材料相比,导热
曲运动。由图 11c 可知,散热片处于伸直和弯曲的 性能增强,升降温速率提高了 1.76 倍,PU/APDMS-1/
状态时,贴附于表面的 PU/APDMS-1/CNTs 的温度 CNTs 有效地将模拟柔性芯片的散热片表面温度
分布是很均匀的,且不受散热片运动影响。 (40、50、60、70、80 ℃)降低了 2.4、7.2、8.0、9.9、
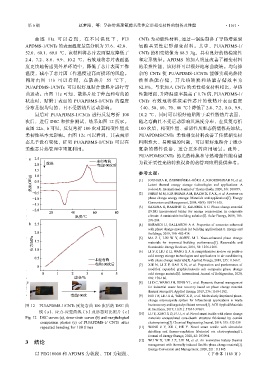
最后对 PU/APDMS-1/CNTs 进行反复弯折 100 10.2 ℃,同时可以很好地贴附于柔性散热片表面,
次后,进行 DSC 和拉伸测试,结果如图 12 所示。 随之弯曲且不受运动影响其温度分布,在反复弯折
由图 12a、b 可见,反复弯折 100 次对其相变性能及 100 次后,相变性能、柔韧性及形态仍能保持原状。
柔韧性基本无影响。由图 12c 可以看到,其表面形 PU/APDMS/CNTs 柔性相变材料改善了传统相变材
态几乎没有变化,证明 PU/APDMS-1/CNTs 可以在 料刚性大、易断裂的问题,可以更好地贴合于微小
柔性芯片热管理中重复利用。 复杂的器件设备,适合更多的应用场景。此外,
PU/APDMS/CNTs 的光热转换和导热增强性能有望
为设计柔性光热转换设备的热管理应用提供参考。
参考文献:
[1] JOUHARA H, ŻABNIEŃSKA-GÓRA A, KHORDEHGAH N, et al.
Latent thermal energy storage technologies and applications: A
review[J]. International Journal of Thermofluids, 2020, 5/6: 100039.
[2] FARID M M, KHUDHAIR A M, RAZACK S A K, et al. A review on
phase change energy storage: Materials and applications[J]. Energy
Conversion and Management, 2004, 45(9): 1597-1615.
[3] SAXENA R, RAKSHIT D, KAUSHIK S C. Phase change material
(PCM) incorporated bricks for energy conservation in composite
climate: A sustainable building solution[J]. Solar Energy, 2019, 183:
276-284.
[4] BERARDI U, GALLARDO A A. Properties of concretes enhanced
with phase change materials for building applications[J]. Energy and
Buildings, 2019, 199: 402-414.
[5] MA Z J, LIN W Y, SOHEL M I. Nano-enhanced phase change
materials for improved building performance[J]. Renewable and
Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 58: 1256-1268.
[6] LI S F, LIU Z H, WANG X J. A comprehensive review on positive
cold energy storage technologies and applications in air conditioning
with phase change materials[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 255: 113667.
[7] XIE N, LI Z P, GAO X N, et al. Preparation and performance of
modified expanded graphite/eutectic salt composite phase change
cold storage material[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2020,
110: 178-186.
[8] LI D C, WANG J H, DING Y L, et al. Dynamic thermal management
for industrial waste heat recovery based on phase change material
thermal storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 236: 1168-1182.
[9] NIU J F, LIU H A, WANG X D, et al. Molecularly imprinted phase-
change microcapsule system for bifunctional applications in waste
图 12 PU/APDMS-1/CNTs 反复弯曲 100 次后的 DSC 曲 heat recovery and targeted pollutant removal[J]. ACS Applied Materials
& Interfaces, 2019, 11(41): 37644-37664.
线(a)、应力-应变曲线(b)及形态对比照片(c) [10] LU Y, XIAO X D, FU J, et al. Novel smart textile with phase change
Fig. 12 DSC curves (a), stress-strain curves (b) and morphological materials encapsulated core-sheath structure fabricated by coaxial
comparison photos (c) of PU/APDMS-1/ CNTs after electrospinning[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 355: 532-539.
repeated bending for 100 times [11] WANG J Y, XU J, HE Y. Novel smart textile with ultraviolet
shielding and thermo-regulation fabricated via electrospinning[J].
Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 42: 103094.
3 结论 [12] WU W X, LIU J Z, LIU M, et al. An innovative battery thermal
management with thermally induced flexible phase change material[J].
Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 221: 113145.
以 PEG10000 和 APDMS 为软段、TDI 为硬段、 (下转第 1189 页)