Page 229 - 《精细化工》2020年第12期
P. 229
第 12 期 侯胜珍,等: 基于动态硼酸酯键改性黄原胶的性能 ·2591·
2–
2–
是由于矿化水中存在 CO 3 和 HCO 3 ,使得溶液呈现 co-AMBB),其与黄原胶通过形成动态硼酸酯键制备
弱碱性,使硼酸根得到更好的活化,与黄原胶的结 了具有微交联结构的改性黄原胶,主要结论如下:
构单元间的结合能力更强,表现出更强的增黏性。 (1)合成了功能单体 AMBB,将其与 AM、
2.2.5 复配体系的抗干扰性 DMAPAM 在水溶液中通过 AIBA 引发自由基共聚,
硼酸基团与黄原胶结构单元中的羟基通过形成 合成了 3 种 P(AM-co-DMAPAM-co-AMBB)样品。通
1
动态硼酸酯键实现微交联增黏,但在实际应用过程 过 HNMR、FTIR 及元素分析确定了共聚物为三元
中,若环境中有顺式 1,2-二醇或者 1,3-二醇结构的 共聚物,并通过光散射测得共聚物的 M w 皆在 1.00
5
多元醇及其衍生物存在,多元醇可能会与硼酸反应 ×10 以下,具有较好的溶解性。
形成五元或六元环状结构,进而影响硼酸共聚物对 (2)P(AM-co-DMAPAM-co-AMBB)与黄原胶复
黄原胶的增黏性。基于此,分别向复配体系中加入 配后对黄原胶溶液具有明显的增黏性。其中,样品
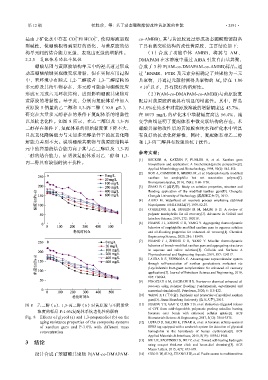
黄原胶 5 倍量的乙二醇和 1,3-丙二醇(10.0 g/L), P-1.0%在纯水中对黄原胶溶液的增黏幅度达 43.7%,
研究在大量多元醇存在的条件下复配体系的增黏性 在 8073 mg/L 的矿化水中增黏幅度高达 56.4%,流
以及抗老化性。如图 8 所示,在乙二醇以及 1,3-丙 变学曲线证明了复配体系中微交联结构的存在。苯
二醇存在条件下,复配体系的初始黏度值下降不大, 硼酸共聚物改性后的黄原胶在纯水和矿化水中皆具
且抗老化降解能力与未加多元醇条件下的抗老化降 有良好的抗老化降解性,同时,复配体系对乙二醇
解能力差别不大。说明硼酸共聚物与黄原胶结构单 和 1,3-丙二醇具有较强的抗干扰性。
元中的羟基的结合能力高于其与乙二醇以及 1,3-丙
参考文献:
二醇的结合能力,证明该复配体系对乙二醇和 1,3-
[1] BECKER A, KATZEN F, PUHLER A, et al. Xanthan gum
丙二醇具有较强的抗干扰性。 biosynthesis and application: A biochemical/genetic perspective[J].
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1998, 50(2): 145-152.
[2] ROY A, COMESSE S, GRISEL M, et al. Hydrophobically modified
xanthan: An amphiphilic but not associative polymer[J].
Biomacromolecules, 2014, 15(4): 1160-1170.
[3] JIANG B C (蒋笔翠). Study on solution properties, structure and
flooding application of the modified xanthan gum[D]. Chengdu:
Chengdu University of Technology (成都理工大学), 2012.
[4] ABDO M. Waterflood oil recovery process employing stablized
biopolymers: US4141842A[P]. 1979-02-27.
[5] CORREDOR L M, HUSEIN M M, MAINI B B. A review of
polymer nanohybrids for oil recovery[J]. Advances in Colloid and
Interface Science, 2019, 272: 102018.
[6] HUANG J J, ZHONG C R, YANG Y. Aggregating thermodynamic
behavior of amphiphilic modified xanthan gum in aqueous solution
and oil-flooding properties for enhanced oil recovery[J]. Chemical
Engineering Science, 2020, 216: 115476.
[7] HUANG J J, ZHONG C R, YANG Y. Micellar thermodynamic
behavior of branch-modified xanthan gum and aggregating structures
in aqueous and saline solutions[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A
Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 587: 124317.
[8] LAURA R Z, ESPINOSA C. Advantageous supramolecular system
through self-association of xanthan gum/cationic surfactant via
β-cyclodextrin host-guest complexations for enhanced oil recovery
applications[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019,
185: 106644.
[9] FIROZJAII A M, SAGHAFI H R. Review on chemical enhanced oil
recovery using polymer flooding: Fundamentals, experimental and
numerical simulation[J]. Petroleum, 2020, 6: 115-122.
[10] WANG X J (王小金). Synthesis and properties of modified xanthan
gum[D]. Jinan: Shandong University (山东大学), 2015.
图 8 乙二醇(a)、1,3-丙二醇(b)对黄原胶与不同质量 [11] HUANG Y S, GAO Y, CHEN T D, et al. Reduction-triggered release
of CPT from acid-degradable polymeric prodrug micelles bearing
浓度的样品 P-1.0%复配体系抗老化性的影响 boronate ester bonds with enhanced cellular uptake[J]. ACS
Fig. 8 Effects of glycol (a) and 1,3-propanediol (b) on the Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2017, 3(12): 3364-3375.
aging resistance properties of the composite systems [12] USTA D D, SALIMI K, PINAR A, et al. A boronate affinity-assisted
of xanthan gum and P-1.0% with different mass SERS tag equipped with a sandwich system for detection of glycated
concentration hemoglobin in the hemolysate of human erythrocytes[J]. ACS
Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(19): 11934-11944.
3 结论 [13] HE L R, SZOPINSKI D, WU Y, et al. Toward self-healing hydrogels
using one-pot thiol-ene click and borax-diol chemistry[J]. ACS
Macro Letters, 2015, 4(7): 673-678.
设计合成了苯硼酸共聚物 P(AM-co-DMAPAM- [14] GUO R W, SU Q, ZHANG J W, et al. Facile access to multisensitive