Page 76 - 《精细化工》2023年第9期
P. 76
·1924· 精细化工 FINE CHEMICALS 第 40 卷
聚苯胺尼龙导电织物在拉伸-回复过程中,纤维 更多,织物导电性更好;
大分子在受到外力作用后会发生普弹形变、高弹形 (2)聚苯胺尼龙导电织物具有良好的拉伸弹性,
变和黏性流动,当外力撤去后,普弹形变迅速完全 当织物受到应力产生形变时,导电性能降低,回缩
恢复,高弹形变逐渐恢复,存在滞后效应。聚苯胺 时恢复;在 15%应变范围内电阻变化率与应变线性
间有效接触未恢复至初始值,织物电流强度略低于 相关性高;当织物受到不同程度和速率的拉伸时都
初始状态。随着纤维间距逐渐回复,聚苯胺导电网 具有良好的稳定性,且经过 3500 次拉伸-回复循环
络逐渐完善,织物电阻随之减小,导电性能提升。 后织物仍具有较好的稳定性;
在食指及手腕做出相似程度的下弯时,5 次测试信 (3)将聚苯胺尼龙导电织物作为传感器贴附于
号波形及强度变化相似,说明聚苯胺尼龙导电织物 手指和手腕上,可实时监测人体关节运动信号;聚
可监测手指、手腕等人体关节部位的运动信号。 苯胺尼龙导电织物塞贝克系数为 8.406 μV/K,可检
2.3.2 温差传感 测织物两端温差。聚苯胺尼龙导电织物作为一种智
室温(20 ℃)下采用自制塞贝克系数测试装置 能可穿戴传感材料,在与电子信息技术相融合后,
测量冷端为 20 ℃、两端温差为 0~40 K 依次变化时 可用于日常对人体运动及体温的实时监测。
聚苯胺尼龙导电织物两端输出电压,结果如图 10 所
2
示。其斜率即为塞贝克系数,并根据 PF=σS 计算出 参考文献:
聚苯胺尼龙导电织物功率因子,其中:PF 为织物功 [1] KHAN Y, OSTFELD A E, LOCHNER C M, et al. Monitoring of
vital signs with flexible and wearable medical devices[J]. Advanced
2
率因子,W/(m·K );σ 为织物电导率,S/m;S 为织 materials, 2016, 28(22): 4373-4395.
物塞贝克系数,μV/K。 [2] AFROJ S, KARIM N, WANG Z H, et al. Engineering graphene
flakes for wearable textile sensors via highly scalable and ultrafast
yarn dyeing technique[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(4): 3847-3857.
[3] LIU M M, PU X, JIANG C Y, et al. Large-area all-textile pressure
sensors for monitoring human motion and physiological signals[J].
Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(41): 1703700.
[4] YANG Q, WANG X, DING X, et al. Fabrication and characterization
of wrapped metal yarns-based fabric temperature sensors[J]. Polymers,
2019, 11(10): 1549
[5] LU X, SHANG W H, CHEN G K, et al. Environmentally stable,
highly conductive, and mechanically robust metallized textiles[J].
ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2021, 3(3): 1477-1488.
[6] WANG C L (王晨露), MA J X (马金星), YANG Y Q (杨雅晴), et al.
Strain sensing property and respiration monitoring of polyaniline-
coated warp-knitted fabrics[J]. Journal of Textile Research (纺织学
报), 2022, 43(8): 113-118.
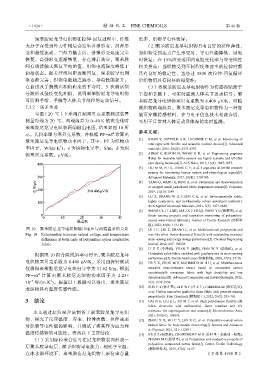
图 10 聚苯胺尼龙导电织物输出电压与两端温差的关系 [7] LV J C, LIU Z, ZHANG L, et al. Multifunctional polypyrrole and
Fig. 10 Relationship between output voltage and temperature rose-like silver flower-decorated E-textile with outstanding pressure/
difference at both ends of polyaniline nylon conductive strain sensing and energy storage performance[J]. Chemical Engineering
fabric Journal, 2022, 427: 130823.
[8] LI Z Z (李泽钊), YUAN Y (原韵), HAN W Y (韩玮屹), et al.
根据图 10 拟合曲线斜率可得出,聚苯胺尼龙导 Conductive nylon fabric modified with graphene and its strain sensing
performances[J]. Textile Auxiliaries (印染助剂), 2020, 37(5): 27-30.
电织物塞贝克系数为 8.406 μV/K。采用四探针测试 [9] HE Y X, ZHOU M Y, MAHMOUD M H H, et al. Multifunctional
仪测得聚苯胺尼龙导电织电导率为 31.62 S/m。根据 wearable strain/pressure sensor based on conductive carbon
2
PF=σS 计算出聚苯胺尼龙织物功率因子为 2.23× nanotubes/silk nonwoven fabric with high durability and low
detection limit[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2022,
2
10 –9 W/(m·K )。根据以上数据可以得出,聚苯胺尼 5(3): 1939-1950.
[10] SUN C Y (孙才英), LYU W F (吕文丰), CIRENDAJIE (次仁达杰),
龙织物具有温度传感性能。
et al. Carbon nanotubes grafted to linen fabric with pressure sensing
properties[J]. Fine Chemicals (精细化工), 2022, 39(2): 295-301.
3 结论 [11] CAI H H, LIU Z L, XU M T, et al. High performance flexible silk
fabric electrodes with antibacterial, flame retardant and UV
本文通过原位聚合法制备了聚苯胺尼龙导电织 resistance for supercapacitors and sensors[J]. Electrochimica Acta,
2021, 390(10): 138895.
物,探究了反应温度、应变、拉伸次数、拉伸速率 [12] ZHOU X R, HU C Y, LIN X C, et al. Polyaniline-coated cotton
对织物导电性能的影响,并测试了将其作为应力和 knitted fabric for body motion monitoring[J]. Sensors and Actuators
A: Physical, 2021, 321: 112591.
温度传感器的可能性,得出以下主要结论: [13] KE G Z (柯贵珍), CHOWDHURY M H (乔杜里·莫法塞·哈克),
(1)采用原位聚合法可在尼龙织物表面形成一 ZHANG M Z (张明卓), et al. Preparation and conductive property of
polyaniline composited cotton fabric[J]. Cotton Textile Technology
层聚苯胺导电层,赋予织物导电能力,相比于室温,
(棉纺织技术), 2019, 47(4): 14-17.
在冰水浴环境下,聚苯胺在尼龙织物上原位聚合量 (下转第 1958 页)