Page 149 - 201906
P. 149
第 6 期 常柄权,等: 变叶海棠叶总黄酮的分离纯化及体外抗炎活性 ·1155·
to the stretching vibration of C—O—C groups (1125~
–1
–1
–1
940 cm ). The peaks at 892.97 cm and 829.32 cm
indicate that the flexural vibration of C==C—H groups
–1
in FMTs (900~650 cm ) might exist.
3.9 Effects of FMTs on the macrophage
inflammatory response
3.9.1 Effects of FMTs on the Viability of RAW
264.7 Macrophages
Inflammation is an integral part of the complex
biological interactions that arise in any tissues in
response to bacterial, chemical or physical injury.
During the inflammatory response, monocyte-
differentiated macrophages produce pro-inflammatory
cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and
tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), as well as low-
molecular-weight mediators such as nitric oxide (NO)
via inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Macrophages
express a large number of pattern recognition
receptors, and they can be activated directly by the
pathogens associated with molecular patterns or their
products. Murine macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells
are commonly used for research on the anti-
inflammatory response [28-31] . The cell viability was
measured based on the formation of blue formazan,
which is metabolized from colourless MTT by
mitochondrial dehydrogenases, enzymes that are only
active in live cells [32] . The cytotoxicity of FMTs on
RAW 264.7 macrophages was determined through the
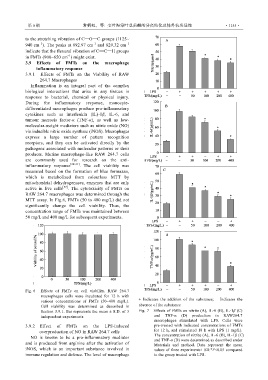
MTT assay. In Fig.6, FMTs (50 to 400 mg/L) did not
significantly change the cell viability. Thus, the
concentration range of FMTs was maintained between
50 mg/L and 400 mg/L for subsequent experiments.
Fig. 6 Effects of FMTs on cell viability. RAW 264.7
macrophages cells were incubated for 12 h with
various concentrations of FMTs (50~400 mg/L). + Indicates the addition of the substance; Indicates the
Cell viability was determined as described in absence of the substance
Section 3.9.1. Bar represents the mean ± S.D. of 3 Fig. 7 Effects of FMTs on nitrite (A), IL-6 (B), IL-1β (C)
independent experiments. and TNF-α (D) production in RAW264.7
macrophages stimulated with LPS. Cells were
3.9.2 Effect of FMTs on the LPS-induced pre-treated with indicated concentrations of FMTs
overproduction of NO in RAW 264.7 cells for 12 h, and stimulated 18 h with LPS (1 mg/L).
NO is known to be a pro-inflammatory mediator The concentration of nitrite (A), IL-6 (B), IL-1β (C)
and is produced from arginine after the activation of and TNF-α (D) were determined as described under
Materials and method. Data represent the mean
iNOS, which is an important substance involved in values of three experiments± SD.*P<0.05 compared
immune regulation and defence. The level of macrophage to the group treated with LPS.