Page 86 - 201907
P. 86
·1332· 精细化工 FINE CHEMICALS 第 36 卷
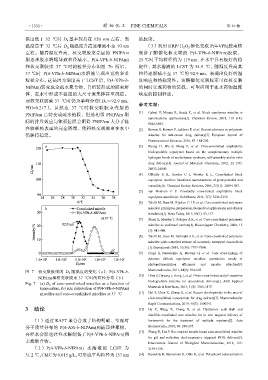
温度低于 32 ℃时 D h 基本保持在 120 nm 左右,当 的胶束。
温度高于 32 ℃后 D h 随温度升高逐渐减小至 93 nm (3)利用 HRP/ H 2 O 2 催化交联 P(4-VPh)胶束核
左右。随着温度升高,核交联胶束壳层的 PNIPAm 制备了酶催化核交联的 P(4-VPh-b-NIPAm)胶束,
刷逐步脱水坍塌导致粒径减小。P(4-VPh-b-NIPAm) 25 ℃时平均粒径约为 119 nm,在水中具有极好的稳
和核交联胶束 37 ℃时的粒径分布如图 7b 所示, 定性,其水溶液的 LCST 为 34.9 ℃,随温度升高其
37 ℃时 P(4-VPh-b-NIPAm)水溶液呈现出宽的多重 粒径逐渐减小至 37 ℃的 92.9 nm,表现出良好的温
粒径分布。这是因为温度高于 LCST 后,P(4-VPh-b- 度响应和热稳定性。该酶催化交联胶束可在核交联
NIPAm)转变成全疏水聚合物,自组装形成的胶束解 的同时实现药物的装载,可望应用于疏水药物温度
体,在水中形成不稳定的大尺寸聚集体甚至沉淀。 响应的控制释放。
而核交联胶束 37 ℃时仍为单峰分布(D h ≈92.9 nm,
参考文献:
PDI=0.217)。虽然在 37 ℃时核交联胶束壳层的
PNIPAm 已转变成疏水链段,但是相邻 PNIPAm 刷 [1] Cabral H, Miyata K, Osada K, et al. Block copolymer micelles in
nanomedicine applications[J]. Chemical Review, 2018, 118 (14):
间的排斥效应与体积位阻会阻碍 PNIPAm 大分子链
6844-6892.
在胶束核表面的完全坍塌,使得核交联胶束在水中 [2] Biswas S, Kumari P, Lakhani P, et al. Recent advances in polymeric
仍保持稳定。 micelles for anti-cancer drug delivery[J]. European Journal of
Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2016, 83: 184-202.
[3] Kuang H, Wu S, Meng F, et al. Core-crosslinked amphiphilic
biodegradable copolymer based on the complementary multiple
hydrogen bonds of nucleobases: synthesis, self-assembly and in vitro
drug delivery[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22 (47):
24832-24840.
[4] O'Reilly R K, Hawker C J, Wooley K L. Cross-linked block
copolymer micelles: functional nanostructures of great potential and
versatility[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2006, 35(11): 1068-1083.
[5] van Nostrum C F. Covalently cross-linked amphiphilic block
copolymer micelles[J]. Soft Matter, 2011, 7(7): 3246-3259.
[6] Talelli M, Barz M, Rijcken C J F, et al. Core-crosslinked polymeric
micelles: principles, preparation, biomedical applications and clinical
translation[J]. Nano Today, 2015, 10(1): 93-117.
[7] Shuai X, Merdan T, Schaper A K, et al. Core-cross-linked polymeric
micelles as paclitaxel carriers[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2004, 15
(3): 441-448.
[8] Talelli M, Iman M, Varkouhi A K, et al. Core-crosslinked polymeric
micelles with controlled release of covalently entrapped doxorubicin
[J]. Biomaterials 2010, 31(30): 7797-7804.
[9] Piogé S, Nesterenko A, Brotons G, et al. Core cross-linking of
dynamic diblock copolymer micelles: quantitative wtudy of
photopolymerization efficiency and micelle structure[J].
图 7 核交联胶束的 D h 随温度的变化(a);P(4-VPh-b- Macromolecules, 2011, 44(3): 594-603.
[10] Chen J, Ouyang J, Kong J, et al. Photo-cross-linked and pH-sensitive
NIPAm)和核交联胶束 37 ℃时的粒径分布(b)
biodegradable micelles for doxorubicin delivery[J]. ACS Applied
Fig. 7 (a) D h of core-crosslinked micelles as a function of
temperature, (b) size distribution of P(4-VPh-b-NIPAm) Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5 (8): 3108-3117.
micelles and core-crosslinked micelles at 37 ℃ [11] Dai Y, Chen X, Zhang X, et al. Recent developments in the area of
click-crosslinked nanocarriers for drug delivery[J]. Macromolecular
Rapid Communications, 2019, 40(3): 1800541.
3 结论 [12] Gu Z, Wang X, Cheng R, et al. Hyaluronic acid shell and
disulfide-crosslinked core micelles for in vivo targeted delivery of
(1)通过 RAFT 聚合合成了结构明确、窄相对 bortezomib for the treatment of multiple myeloma[J]. Acta
分子质量分布的 P(4-ASt-b-NIPAm)两嵌段共聚物, Biomaterialia, 2018, 80: 288-295.
[13] Zhang H, Liu P. Bio-inspired keratin-based core-crosslinked micelles
再经水合肼选择性水解制备了 P(4-VPh-b-NIPAm)两
for pH and reduction dual-responsive triggered DOX delivery[J].
亲性聚合物。 International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 123:
( 2) P(4-VPh-b-NIPAm) 水溶 液的 LCST 为 1150-1156.
31.2 ℃,CMC 为 0.015 g/L,可形成平均粒径为 137 nm [14] Kawakita H, Hamamoto K, Ohto K, et al. Polyphenol polymerization