Page 229 - 精细化工2020年第2期
P. 229
第 2 期 杨环毓,等: 红茶、绿茶提取物的协同护肤功效 ·431·
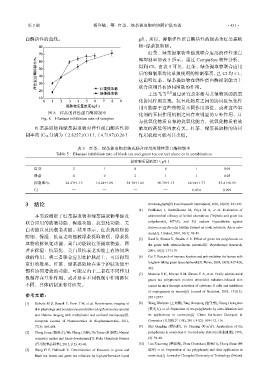
白酶活性的曲线。 g/L,所以,抑制弹性蛋白酶活性的强弱为红茶提取
物>绿茶提取物。
红茶、绿茶提取物单独或联合应用的弹性蛋白
酶抑制率如表 5 所示。通过 CompuSyn 软件分析,
得到 CI。由表 5 可见,红茶、绿茶提取物联合应用
后的抑制率均比单独使用的抑制率高,且 CI 均<1,
这说明红茶、绿茶提取物在弹性蛋白酶抑制能力上
联合应用具有协同增效的作用。
王岳飞等 [25] 通过研究茶多酚与其他物质的抗氧
化协同作用发现,抗氧化物质之间的协同抗氧化作
用可能源于这些药物是不同作用部位,或者这些氧
图 8 样品的弹性蛋白酶抑制率 化剂的不同作用机制之间存在明显的互补作用,且
Fig. 8 Elastase inhibition rate of samples
与抗氧化物质自身的抗氧化能力,抗氧化物质有效
红茶提取物和绿茶提取物对弹性蛋白酶活性抑 浓度的高低等因素有关。红茶、绿茶提取物的协同
制率的 IC 50 分别为(2.8257±0.11)、(4.7197±0.26) 作用机理可能与其类似。
表 5 红茶、绿茶提取物单独或联合应用的弹性蛋白酶抑制率
Table 5 Elastase inhibition rate of black tea and green tea extract alone or in combination
提取物质量浓度/(g/L)
红茶 2 1 0 0 1 0.05
绿茶 0 0 2 1 1 0.05
抑制率/% 24.27±1.15 18.24±1.09 38.70±1.09 30.79±1.13 68.94±1.77 53.41±0.93
CI — — — — 0.054 0.099
3 结论 chromatography[J]. Food Research International, 2001, 34(2/3): 223-227.
[4] Prabhakar J, Senthilkumar M, Priya M S, et al. Evaluation of
本实验测定了红茶提取物和绿茶提取物单独及 antimicrobial efficacy of herbal alternatives (Triphala and green tea
联合应用的防晒功能、保湿功能、抗氧化功能、美 polyphenols), MTAD, and 5% sodium hypochlorite against
Enterococcus faecalis biofilm formed on tooth substrate: An in vitro
白功能以及抗衰老功能。结果显示,红茶提取物的
study[J]. J Endod, 2010, 36(1): 83-86.
防晒、保湿、抗衰老功能较绿茶提取物强,绿茶提
[5] Kaul D, Sikand K, Shukla A R. Effect of green tea polyphenols on
取物的抗氧化功能、美白功能较红茶提取物强,两 the genes with atherosclerotic potential[J]. Phytotherapy Research,
者在保湿、抗氧化、美白及抗衰老功能上有协同增 2004, 18(2): 177-179.
效的作用,将二者联合应用在护肤品上,可以得到 [6] Cui Y. Research of immune function and anti-oxidation for human with
更好的效果。红茶、绿茶提取物在多个护肤功能中 longterm taking green tea polyphenols[J]. Tumor, 2004, 24(5): 427-428,
432.
都有协同增效的功能,可能是由于二者在不同作用
[7] Mantena S K, Meeran S M, Elmets C A, et al. Orally administered
机制存在互补作用,或者是在不同机制中作用部位 green tea polyphenols prevent ultraviolet radiation-induced skin
不同,具体机制还有待研究。 cancer in mice through activation of cytotoxic T cells and inhibition
of angiogenesis in tumors[J]. Journal of Nutrition, 2005, 135(12):
参考文献: 2871-2877.
[1] Roberts M S, Dancik Y, Prow T W, et al. Non-invasive imaging of [8] Wang Wenyuan (王文渊), Tang Shouyong (唐守勇), Huang Guangwen
skin physiology and percutaneous penetration using fluorescence spectral (黄光文), et al. Separation of tea-polyphenols by ultra filtration and
and lifetime imaging with multiphoton and confocal microscopy[J]. its applications in cosmetics[J]. China Surfactant Detergent &
European Journal of Pharmaceutics & Biopharmaceutics, 2011, Cosmetics (日用化学工业), 2011, 41(2): 109-112, 116.
77(3): 469-488. [9] Shu Qingling (舒庆龄), Ye Yunqing (叶运青). Application of tea
[2] Zhang Jincai (张进才), Wu Zheng (吴峥), Du Tairan (杜泰然). Natural polyphenols in cosmetics[J]. Tea Industry Bulletin (茶业通报), 1996,
cosmetics market and future development[J]. Daily Chemicals Science (2): 39-40.
(日用化学品科学), 2012, (12): 43-46. [10] Luo Xiaoming (罗晓明), Zhou Chunshan (周春山), Zhong Shian (钟
[3] Wang H F, Helliwell K. Determination of flavonols in green and 世安) et al. Preparation of tea polyphenols and their application in
black tea leaves and green tea infusions by high-performance liquid cosmetics[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Technology (Natural