Page 125 - 《精细化工》2022年第10期
P. 125
第 10 期 袁 帆,等: 黏膜黏附性缺氧响应型壳聚糖胶束的制备与性能 ·2059·
up-to-date review[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 319:
135-156.
[4] LI Y C, JEON J, PARK J H. Hypoxia-responsive nanoparticles for
tumor-targeted drug delivery[J]. Cancer Letters, 2020, 490: 31-43.
[5] CHEN Y, ZHANG X, LU X Y, et al. Ultra-sensitive responsive
near-infrared fluorescent nitroreductase probe with strong specificity
for imaging tumor and detecting the invasiveness of tumor cells[J].
Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular
Spectroscopy, 2022, 268: 120634.
[6] LI Y, LU A, LONG M, et al. Nitroimidazole derivative incorporated
liposomes for hypoxia-triggered drug delivery and enhanced
therapeutic efficacy in patient-derived tumor xenografts[J]. Acta
Biomaterialia, 2019, 83: 334-348.
[7] THAMBI T, DEEPAGAN V G, YOON H Y, et al. Hypoxia-
responsive polymeric nanoparticles for tumor-targeted drug
delivery[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35 (5): 1735-1743.
[8] HE H, ZHU R Y, SUN W, et al. Selective cancer treatment via
photodynamic sensitization of hypoxia-responsive drug delivery[J].
Nanoscale, 2018, 10 (6): 2856-2865.
[9] AHMAD Z, LYU S, TANF Z, et al. Methoxy poly (ethylene
glycol)-block-poly (glutamic acid)-graft-6-(2-nitroimidazole) hexyl
amine nanoparticles for potential hypoxia-responsive delivery of
doxorubicin[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition,
2016, 27 (1): 40-54.
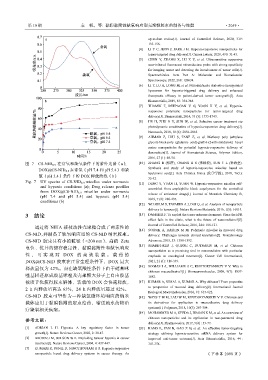
图 7 CS-NID 8.9 在常氧和缺氧条件下的紫外光谱(a); [10] ZHANG B (张蓓), CHANG B S (常柏松), SUN T L (孙涛垒).
DOX@CS-NID 8.9 在常氧(pH 7.4 和 pH 5.4)和缺 Synthesis and study of hypoxia-responsive micelles based on
hyaluronic acid[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica (化学学报), 2018, 76(1):
氧(pH 5.4)条件下的 DOX 释放曲线(b)
35-42.
Fig. 7 UV spectra of CS-NID 8.9 micelles under normoxic [11] DENG Y, YUAN H, YUAN W. Hypoxia-responsive micelles self-
and hypoxic conditions (a); Drug release profiles assembled from amphiphilic block copolymers for the controlled
from DOX@CS-NID 8.9 micelles under normoxic
(pH 7.4 and pH 5.4) and hypoxic (pH 5.4) release of anticancer drugs[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,
conditions (b) 2019, 7 (2): 286-295.
[12] WILHELM S, TAVARES A J, DAI Q, et al. Analysis of nanoparticle
delivery to tumours[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2016, 1(5): 16014.
3 结论 [13] DANHIER F. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Since the EPR
effect fails in the clinic, what is the future of nanomedicine?[J].
Journal of Controlled Release, 2016, 244: 108-121.
通过将 NIHA 接枝改性壳聚糖合成了两亲性的
[14] SOSNIK A, RASKIN M M. Polymeric micelles in mucosal drug
CS-NID,并制备了缺氧响应型的 CS-NID 纳米胶束。 delivery: Challenges towards clinical translation[J]. Biotechnology
CS-NID 胶束具有小的粒径(<200 nm)、高的 Zeta Advances, 2015, 33: 1380-1392.
[15] SHARIFI-RED J, QUISPE C, BUTNARIU M, et al. Chitosan
电位、优异的储存稳定性、黏膜黏附性和缺氧响应
nanoparticles as a promising tool in nanomedicine with particular
性 ,可实现 对 DOX 的 高效装 载。载药 的 emphasis on oncological treatment[J]. Cancer Cell International,
DOX@CS-NID 胶束在正常生理条件下,DOX 最大 2021, 21 (1): 318-339.
释放量仅为 42%。而在缺氧酸性条件下由于硝基咪 [16] SOGIAS I A, WILLIAMS A C, KHUTORYANSKIY V V. Why is
chitosan mucoadhesive?[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2008, 9(7): 1837-
唑基团还原成胺基咪唑及壳聚糖大分子上自由胺基 1842.
被质子化使得胶束解体,装载的 DOX 会快速释放, [17] KUMAR A, VIMAL A, KUMAR A. Why chitosan? From properties
to perspective of mucosal drug delivery[J]. International Journal
2 h 内释放量高达 65%,24 h 内释放量超过 92%。
Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 91: 615-622.
CS-NID 胶束可望作为一种缺氧微环境响应的纳米 [18] WAYS T M M, LAU W M, KHUTORYANSKIY V V. Chitosan and
载体应用于黏膜黏附的定点给药,输送疏水药物治 its derivatives for application in mucoadhesive drug delivery
systems[J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(3): 267-304.
疗缺氧相关疾病。
[19] MOHAMMED M A, SYEDA J, WASAN K M, et al. An overview of
chitosan nanoparticles and its application in non-parenteral drug
参考文献:
delivery[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2017, 9(4) : 53-79.
[1] ADRIAN L H. Hypoxia—A key regulatory factor in tumor [20] KANG L, FAN B, GAO Z G, et al. An effective tumor-targeting
growth[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2002, 2: 38-47. strategy utilizing hypoxia-sensitive siRNA delivery system for
[2] BROWN J M, WILSON W R. Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer improved anti-tumor outcome[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2016, 44 :
treatment[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2004, 4: 437-447. 341-354.
[3] KUMARI R, SUNIL D, NINGTHOUJAM R S. Hypoxia-responsive
nanoparticle based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy: An (下转第 2098 页)