Page 139 - 《精细化工》2022年第9期
P. 139
第 9 期 黄冬婷,等: 超声辅助离子液体提取人参多糖工艺及其抗氧化活性 ·1857·
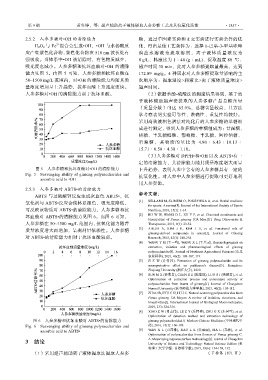
2.5.2 人参多糖对•OH 的清除能力 糖,通过单因素实验和正交实验进行实验条件的优
2+
H 2 O 2 与 Fe 混合会生成•OH,•OH 与水杨酸反 化,得出最佳工艺条件为:选择 1-己基-3-甲基咪唑
应产生紫色化合物,紫色化合物在 510 nm 波长处有 溴盐水溶液为提取溶剂,离子液体质量浓度为
强吸收。当体系中•OH 被清除时,有色物质减少, 8 g/L、料液比为 1∶40 (g∶mL)、提取温度 80 ℃、
吸光度也减小。人参多糖和抗坏血酸对•OH 的清除 超声时间 30 min,此时人参多糖提取量最高,达到
能力见图 5。由图 5 可知,人参多糖和抗坏血酸在 172.89 mg/g。4 种因素对人参多糖提取量影响的主
50~1500 mg/L 范围内,对•OH 的清除能力均随其质 次顺序为:提取温度>料液比>离子液体质量浓度>
量浓度增加呈上升趋势,抗坏血酸上升速度更快。 超声时间。
人参多糖对•OH 的清除能力弱于抗坏血酸。 (2)依据苯酚-硫酸法的测定结果得到,基于离
子液体辅助超声法提取的人参多糖产品总糖含量
(质量分数)可达 65.9%,总糖含量较高,且方法
学考察表明实验可靠性、准确性、重复性均较好。
采用高效液相色谱法对纯化后的人参多糖的单糖组
成进行测定,得到人参多糖的单糖组成为:甘露糖、
核糖、半乳糖醛酸、葡萄糖、半乳糖、阿拉伯糖、
岩 藻 糖 ,其物 质的 量比为 4.80∶ 6.43∶ 10.13∶
15.71∶0.50∶4.30∶1.10。
(3)人参多糖对 DPPH•和•OH 以及 ABTS•有一
定的清除能力,其清除能力随其质量浓度增大而呈
图 5 人参多糖和抗坏血酸对•OH 的清除能力 上升趋势,表明人参中含有的人参多糖具有一定的
Fig. 5 Scavenging ability of ginseng polysaccharides and 抗氧化性。对人参中人参多糖进行提取可更好地利
ascorbic acid to •OH
用人参资源。
2.5.3 人参多糖对 ABTS•的清除能力
参考文献:
ABTS 与过硫酸钾反应生成灰蓝色 ABTS•,抗
氧化剂与 ABTS•反应会使体系褪色,吸光度降低, [1] SELLAMI M, SLIMENI O, POKRYWKA A, et al. Herbal medicine
for sports: A review[J]. Journal of the International Society of Sports
可反映该物质对 ABTS•的清除能力,人参多糖和抗 Nutrition, 2018, 15(1): 1-14.
[2] RU W W, WANG D L, XU Y P, et al. Chemical constituents and
坏血酸对 ABTS•的清除能力见图 6。由图 6 可知,
bioactivities of Panax ginseng (CA Mey.)[J]. Drug Discoveries &
人参多糖在 50~1500 mg/L 范围内,抗氧化能力随着 Therapeutics, 2015, 9(1): 23-32.
质量浓度增大而增加,呈现剂量依赖性。人参多糖 [3] AHUJA A, KIM J H, KIM J H, et al. Functional role of
ginseng-derived compounds in cancer[J]. Journal of Ginseng
对 ABTS•的清除能力相对于抗坏血酸较弱。 Research, 2018, 42(3): 248-254.
[4] WANG Y M (王一鸣), WANG X L (王兴录). Research progress on
extraction, isolation and pharmacological effects of ginseng
polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences (东北
农业科学), 2021, 46(2): 103-107, 119.
[5] JI Z W (计竹娃). Extraction of ginseng polysaccharide and its
neuroprotective effect on parkinson’s disease[D]. Hangzhou:
Zhejiang University (浙江大学), 2020.
[6] SUN M X (孙萌肖), CHEN R Z (陈瑞战), LUO S J (骆淑君), et al.
Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of
polysaccharides from leaves of ginseng[J]. Journal of Changchun
Normal University (长春师范大学学报), 2021, 40(2): 105-112.
[7] ZHAO B, LYU C N, LU J C. Natural occurring polysaccharides from
Panax ginseng CA Meyer: A review of isolation, structures, and
bioactivities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,
2019, 133: 324-336.
[8] XIAO Z W (肖志伟), LE Z Y (乐智勇), ZHU G X (朱国雪), et al.
Optimization of detection method and extraction technology of
图 6 人参多糖和抗坏血酸对 ABTS•的清除能力 ginseng polysaccharides[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine (中国现代中
Fig. 6 Scavenging ability of ginseng polysaccharides and 药), 2016, 18(1): 106-109.
ascorbic acid to ABTS• [9] WAN X L (万茜淋), JIAO L L (焦丽丽), MA L (马林), et al.
Optimization of polysaccharides from flowers of Panax ginseng C.
3 结论 A. Meyer using response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Changchun
University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition (长
春理工大学学报: 自然科学版), 2015, 38(6): 154-158, 132.
(1)采用超声辅助离子液体提取法提取人参多 (下转第 1871 页)