Page 50 - 201808
P. 50
·1298· 精细化工 FINE CHEMICALS 第 35 卷
时,油酸盐分解速率加快,在 1 h 反应时间内油酸 米粒子形貌转变过程遵循粒子内熟化机理。随着反
盐浓度降低较多,磁性纳米粒子沿多个晶面生长, 应温度提高或反应时间延长,磁性纳米粒子由纺锤
最终产物为不规则的纵横比较小的纳米粒子;当反 状纳米粒子转变为具有棱角的不规则状纳米粒子,
应温度继续升高时,油酸盐分解速率更快,在 1 h 进而磁性纳米粒子的棱角逐渐变得模糊并最终形成
反应时间内油酸盐浓度大幅度下降,磁性纳米粒子 球状磁性纳米粒子。本文为同时调控磁性纳米粒子
发生粒子内熟化过程,最终产物为球状纳米粒子。 的形貌、晶体结构和磁性能提供了实验依据,为制
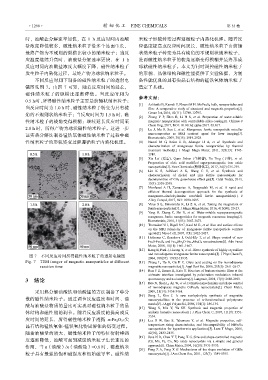
不同反应时间下制备的磁性纳米粒子的透射电 备性能优良的具有尖晶石结构的锰铁氧体纳米粒子
镜图见图 7。由图 7 可知,随着反应时间的延长, 奠定了基础。
磁性纳米粒子的纵横比逐渐降低。当反应时间为
参考文献:
0.5 h 时,所得磁性纳米粒子主要是纺锤状纳米粒子;
[1] Aslibeiki B, Kameli P, Ehsani M H. MnFe 2O 4 bulk, nanoparticles and
当反应时间为 1.0 h 时,磁性纳米粒子转变为具有棱 film: A comparative study of structural and magnetic properties[J].
角的不规则状纳米粒子;当反应时间为 1.5 h 时,磁 Ceram Int, 2016, 42(11): 12789-12795.
[2] Zhang Y P, Zhen B, Li H S, et al. Preparation of water-soluble
性纳米粒子的棱角变得模糊;继续延长反应时间至 magnetic nanoparticles with controllable silica coating[J]. Chinese J
Chem Eng, 2017, DOI: 10.1016/j.cjche.2017. 05.017.
2.0 h 时,所得产物为球状磁性纳米粒子。这进一步 [3] Lu J, Ma S, Sun J, et al. Manganese ferrite nanoparticle micellar
证实热分解法制备锰铁氧体磁性纳米粒子过程中磁 nanocomposites as MRI contrast agent for liver imaging[J].
Biomaterials, 2009, 30(15): 2919-2928.
性纳米粒子的形貌转变过程遵循粒子内熟化机理。 [4] Naseri M G, Saion E B, Ahangar H A, et al. Synthesis and
characterization of manganese ferrite nanoparticles by thermal
treatment method[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2011, 323(13): 1745-
1749.
[5] Xia Lei (夏雷), Quan Jishan (全姬善), Yu Ting (于婷), et al.
Preparation of oleic acid modified superparamagnetic iron oxide
nanoparticles[J]. Fine Chemicals (精细化工), 2017, 34(7):735-739.
[6] Lin K S, Adhikari A K, Wang C Y, et al. Synthesis and
characterization of nickel and zinc ferrite nanocatalysts for
decomposition of CO 2 greenhouse effect gas[J]. Catal Today, 2013,
13(4): 2538-2548.
[7] Monfared A H, Zamanian A, Beygzadeh M, et al. A rapid and
efficient thermal decomposition approach for the synthesis of
manganese-zinc/oleylamine core/shell ferrite nanoparticles[J]. J
Alloy Compd, 2017, 693: 1090-1095.
[8] Vinas S L, Simeonidis K, Li Z A, et al. Tuning the magnetism of
ferrite nanoparticles[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2016, 415(S0): 20-23.
[9] Yang H, Zhang C, Shi X, et al. Water-soluble superparamagnetic
manganese ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging[J].
Biomaterials, 2010, 31(13): 3667-3673.
[10] Tromsdorf U I, Bigall N C, Kaul M G., et al. Size and surface effects
on the MRI relaxivity of manganese ferrite nanoparticle contrast
agents[J]. Nano Lett, 2007, 7(8): 2422-2427.
[11] Hofmann C, Rusakova I, Ould-Ely T, et al. Shape control of new
Fe xO-Fe 3O 4 and Fe 1-yMn yO-Fe 3-zMn zO 4 nanostructures[J]. Adv Funct
Mater, 2008, 18(11): 1661-1667.
[12] Kang E, Park J, Hwang Y, et al. Direct synthesis of highly crystalline
图 7 不同反应时间所得磁性纳米粒子的透射电镜图 and monodisperse manganese ferrite nanocrystals[J]. J Phys Chem B,
2004, 108(37): 13932-13935.
Fig. 7 TEM images of magnetic nanoparticles at different [13] Zhang L, He R, Gu H C. Oleic acid coating on the monodisperse
reaction time magnetite nanoparticles[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2006, 253(5): 2611-2617.
[14] Ren Y Z, Iimura K, Kato T. Structure of barium stearate films at the
air/water interface investigated by polarization modulation infrared
3 结论 spectroscopy and π-a isotherms[J]. Langmuir, 2001, 17(9): 2688-2693.
[15] Bao N, Shen L, An W, et al. Formation mechanism and shape control
of monodisperse magnetic CoFe 2O 4 nanocrystals[J]. Chem Mater,
采用热分解油酸铁和油酸锰的方法制备了单分 2009, 21(14): 3458-3468.
[16] Jiang L, Kim J. A new nonhydrolytic synthesis of magnetite
散的磁性纳米粒子。通过调节反应温度和时间、油 nanocrystallites in the presence of ω-functionalized polystyrene
酸与油酸盐物质的量比可实现对磁性纳米粒子的晶 matrix[J]. J Appl Polym Sci, 2006, 101(1): 186-191.
[17] Wang S, Min Y, Yu SH. Synthesis and magnetic properties of
体结构和磁性能的调节。随着反应温度的提高或反 uniform hematite nanocubes[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111(9): 3551-
3554.
应时间的延长,所得磁性纳米粒子遵循 α-Fe 2 O 3 -尖 [18] Lee S W, Bae S, Takemura Y, et al. Magnetic properties, self-
晶石结构锰铁氧体-锰铁氧化物固溶体的衍变过程。 temperature rising characteristics, and biocompatibility of NiFe 2O 4
nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications[J]. Leee T Magn, 2006,
随着油酸量的增大,磁性纳米粒子的特征衍射峰强 42(10), 2833-2835.
[19] Jana N R, Chen Y F, Peng X G. Size-and shape-controlled magnetic
度逐渐降低,油酸可起到减缓纳米粒子生长速度的 (Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) oxide nanocrystals via a simple and general
作用,当 n(油酸)/n(油酸盐)=0.8 时,磁性纳米 approach[J]. Chem Mater, 2004, 16(20): 3931-3935.
[20] Peng Z A, Peng X G. Mechanisms of the shape evolution of CdSe
粒子具有最强的饱和磁强度和初始磁导率。磁性纳 nanocrystals[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2001, 123(7): 1389-1395.