Page 131 - 《精细化工》2022年第2期
P. 131
第 2 期 李 杰,等: 红脚艾和汤阴北艾精油的化学成分及抗菌活性 ·335·
果较差;而红脚艾精油对 5 种菌株的杀灭效果都较 桉油精、松油烯-4-醇等,桉油精不仅有广泛的抗菌
差。SFE-MD 法提取北艾精油的杀菌效果强于 SD 法。 作用 [19] ,还是一种有效的抗菌增强剂 [25] ,而松油烯-4-
北艾精油的杀菌效果明显比红脚艾精油好。北艾精 醇也具有广泛的杀虫、抑菌功效 [22] ,这可能是汤阴
油中含量丰富且明显高于红脚艾精油的主要成分有 北艾精油的杀菌效果优于红脚艾精油的原因之一。
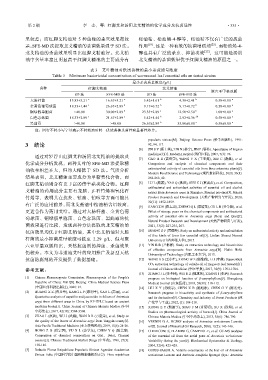
表 3 艾叶精油对供试菌株的最小杀菌质量浓度
Table 3 Minimum bactericidal concentration of wormwood leaf essential oils on tested strains
最小杀菌质量浓度/(g/L)
菌种 红脚艾精油 北艾精油
聚六亚甲基双胍
SD 法 SFE-MD 法 SD 法 SFE-MD 法
a
大肠杆菌 15.83±3.21 c 16.67±3.21 c 5.42±1.61 b 4.38±2.41 b 0.50±0.00
a
金黄色葡萄球菌 18.33±1.44 c 26.67±2.89 d 9.17±0.72 b 9.17±0.72 b 0.50±0.00
a
铜绿假单胞菌 >40.00 30.00±2.89 d 23.33±2.89 c 12.50±2.50 b 1.00±0.00
a
白色念珠菌 18.33±2.89 c 21.67±2.89 c 5.42±1.44 b 2.92±0.36 ab 0.50±0.00
a
黑曲霉 >40.00 >40.00 26.67±2.89 b 35.00±0.00 c 0.50±0.00
注:同行不同小写字母表示不同精油对同一供试菌株杀菌性有显著性差异。
popularis sinicae[M]. Beijing: Science Press (科学出版社), 1991:
3 结论 92, 94, 117.
[6] JIN S Y (靳士英), LIN N (林宁), JIN P (靳朴). Apocalypse of lingnan
medicine(3)[J]. Modern Hospital (现代医院), 2007, 7(3): 76.
通过对罗浮山红脚艾和汤阴北艾精油的提取及
[7] GAO H R (高海荣), WANG Y X (王亚鑫), XIE C (谢晨), et al.
化学成分分析发现,两种艾叶的 SFE-MD 法提取精 Comparison and analysis of chemical components and their
油收率相差不大,但均大幅低于 SD 法。气质分析 antimicrobial activity of essential oils from three artemisia plants[J].
Modern Food Science and Technology (现代食品科技), 2020, 36(1):
结果表明,北艾精油主要成分为单萜类化合物,而 262-268, 42.
红脚艾精油则含有更丰富的倍半萜类化合物。红脚 [8] LU L (路露), YAO Q (姚琪), SHU C J (束成杰), et al. Composition,
antibacterial and antioxidant activities of essential oil and alcohol
艾精油的药用成分主要有龙脑、β-石竹烯和氧化石 extract from Artemisia argyi in Shangluo, Shaanxi province[J]. Natural
竹烯等,表明其在抗炎、镇痛、镇咳等方面可能具 Product Research and Development (天然产物研究与开发), 2020,
32(11): 1852-1859.
有广泛的应用前景,而北艾精油中桉油精含量较高, [9] JIANG Z H (蒋志惠), ZHENG Q L (郑婧龙), GU L B (谷令彪), et al.
更适合作为药用艾叶。通过对大肠杆菌、金黄色葡 Effect of storage years on the chemical components and antibacterial
萄球菌、铜绿假单胞菌、白色念珠菌、黑曲霉的抗 activity of essential oils in Artemisia argyi (Beiai and Qiai)[J].
Natural Product Research and Development (天然产物研究与开发),
菌效果进行比较,发现两种方法提取的北艾精油的 2021, 33(2): 227-235, 207.
抗菌效果均优于红脚艾精油,其中北艾精油对大肠 [10] HUANG D F (黄德峰). Study on antibacterial activity and antioxidation
of five kinds of fever few essential oil[D]. Linfen: Shanxi Normal
杆菌的最小抑菌质量浓度可低至 2.29 g/L,但与聚 University (山西师范大学), 2015.
六亚甲基双胍相比,天然抗菌剂的抑菌、杀菌效果 [11] YIN B B (尹彬彬). Study on extraction technology and bioactivities
of effective components from Artemisia argyi[D]. Hefei: Hefei
仍较差。本文为非道地艾叶的应用推广及新型天然 University of Technology (合肥工业大学), 2015.
抗菌防腐剂的开发提供了数据基础。 [12] WANG X S (王小生), XIONG W Z (熊维政), LI J (李静). Supercritical
CO 2 extraction technology of volatile oil of mugwort leaf research[J].
参考文献: Journal of Chinese Medicine (中医学报), 2017, 32(9): 1701-1704.
[13] ZHANG J L (张季林), WEI H Z (魏惠珍), ZHANG J (张洁). Research
[1] Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's progress on biological function of β-caryophyllene[J]. Shangdong
Republic of China: Vol I[S]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press Medical Journal (山东医药), 2018, 58(38): 110-112.
(中国医药科技出版社), 2020: 91. [14] LIU X Y (刘晓宇), CHEN X B (陈旭冰), CHEN G Y (陈光勇).
[2] HUANG X Z (黄显章), KANG L P (康利平), GAO L (高丽), et al. Research progress in bioactivity and synthesis of β-caryophyllene
Quantative analysis of eupatilin and jaceosidin in folium of Artemisia and its derivatives[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products (林
argyi from different areas in China by RP-HPLC based on ancient 产化学与工业), 2012, (1): 104-110.
medicine books[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica (中国 [15] XIONG Z Y (熊振宇), XIAO F M (肖复明), XU X (徐旭), et al.
中药杂志), 2017, 42(18): 3504-3508. Studies on pharmacological activity of borneol[J]. China Journal of
[3] ZHAO L (赵莉), WU J (武娟), WAN D R (万定荣), et al. Study on Chinese Materia Medica (中国中药杂志), 2013, 38(6): 786-790.
the quality of the leaves of Artemisia argyi from Tangyin county[J]. [16] VERNIN G A. GC/MS analysis of Artemisia verlotiorum Lamotte
Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine (亚太传统医药), 2019, 15(6): 24-26. oil[J]. Journal of Essential Oil Research, 2000, 12(2): 143-146.
[4] HONG Z G (洪宗国), YU X L (余学龙), CHEN Y Q (陈艺球). [17] CHERICONI S, FLAMINI G, CAMPEOL E, et al. GC-MS analyses
Comparison of chemical composition on Qiai, Beiai, Chuanai of the essential oil from the aerial parts of Artemisia verlotiorum:
essence[J]. Chinese Traditional Herbal Drugs (中草药), 1996, 27(3): Variability during the year[J]. Biochemical Systematics & Ecology,
138-140. 2004, 32(4): 423-429.
[5] Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academiae [18] GURIB-FAKIM A. Volatile constituents of the leaf oil of Artemisia
Sinicae Edita (中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会). Flora reipublicae verlotiorum Lamotte and Ambrosia tenuifolia Sprengel (Syn.: Artemisia