Page 66 - 《精细化工》2022年第5期
P. 66
·920· 精细化工 FINE CHEMICALS 第 39 卷
3,4-DCA 的解毒,而本实验证明细菌中同样存在 N- A study on the fate of the priority pollutant in a sediment-water
乙酰基转移酶介导的生物修复系统。 system derived from a rice growing region in Italy[J]. Science of the
Total Environment, 2017, 574: 1012-1020.
[6] CARVALHO G, MARQUES R, LOPES A R, et al. Biological
treatment of propanil and 3,4-dichloroaniline: Kinetic and microbiological
characterisation[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44: 4980-4991.
[7] TASCA A L, FLETCHER A. State of the art of the environmental
behavior and removal techniques of the endocrine disruptor
3,4-dichloroaniline[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health,
Part A, 2018, 53: 260-270.
[8] ZHANG T(张涛), LIU S J(刘双江), LIU Z P(刘志培). A novel
metabolism pathway for the biodegradation of chloroanilines[J].
Microbiology China (微生物学通报), 2007, 47(1): 83-87.
[9] DENG L(邓林), LIU Y L(刘延岭), WANG Z Y(王忠彦), et al.
Screening and identification of a nitrile degrading bacterium strain
and its degradability[J]. Fine Chemicals (精细化工), 2004, 21(12):
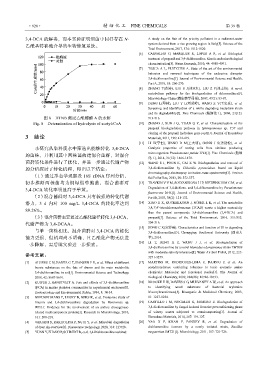
图 8 DTNB 测定乙酰辅酶 A 的水解 913-916.
Fig. 8 Determination of hydrolysis of acetyl-CoA [10] ZHANG J, SUN J Q, YUAN Q Y, et al. Characterization of the
propanil biodegradation pathway in Sphingomonas sp. Y57 and
cloning of the propanil hydrolase gene prpH[J]. Journal of Hazardous
3 结论 Materials, 2011, 196: 412-419.
[11] LI H(李恒), WANG D M(王大明), GONG J S(龚劲松), et al.
本研究从染料废水中筛选出能够转化 3,4-DCA Catalytic properties of resting cells from nitrilase producing
microorganism Pseudomonas putida XY4[J]. Fine Chemicals (精细
的菌株,并利用其中两株菌构建混合菌群,对混合
化工), 2014, 31(12): 1466-1470.
菌群转化条件进行了优化,并进一步通过代谢产物 [12] WANG S J, POON K, CAI Z W. Biodegradation and removal of
的分析探讨了转化机理,得出以下结论: 3,4-dichloroaniline by Chlorella pyrenoidosa based on liquid
chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry[J]. Environ
(1)通过形态学观察及 16S rDNA 序列分析, Sci Pollut Res, 2013, 20: 552-557.
初步推断两株菌均为铜绿假单胞菌,混合菌群对 [13] TRAVKIN V V M, SOLYANIKOVA I I P, RIETJENS I I M C M, et al.
3,4-DCA 转化率明显高于单菌。 Degradation of 3,4-dichloro- and 3,4-difluoroaniline by Pseudomonas
fluorescens 26-K[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health,
(2)混合菌群对 3,4-DCA 具有较强的转化代谢 Part B, 2003, 38(2): 121-132.
潜力,3 d 内对 100 mg/L 3,4-DCA 的转化率达到 [14] XIAO H X, KUCKELKORN J, NÜßER L K, et al. The metabolite
3,4,3ʹ,4ʹ-tetrachloroazobenzene (TCAB) exerts a higher ecotoxicity
89.26%。
than the parent compounds 3,4-dichloroaniline (3,4-DCA) and
(3)混合菌群主要通过乙酰化途径转化 3,4-DCA, propanil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 551/552:
代谢产物为 3,4-DCAA。 304-316.
[15] SONG C X(宋彩霞). Characteristics and function of S1 in degrading
与单一菌株相比,混合菌群对 3,4-DCA 的转化 3,4-dichloroaniline[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University (西南大
能力更强,但机理尚不明确,且乙酰化产物无法进 学), 2014.
一步降解,需后续实验进一步探索。 [16] LI T, DENG X P, WANG J J, et al. Biodegradation of
3,4-dichloroaniline by a novel Myroides odoratimimus strain LWD09
with moderate salinity tolerance[J]. Water Air Soil Pollut, 2012, 223:
参考文献: 3271-3279.
[1] ALBERS C N, BANTA G T, HANSEN P E, et al. Effect of different [17] MARTINS M, RODRIGUES-LIMA F, DAIROU J, et al. An
humic substances on the fate of diuron and its main metabolite acetyltransferase conferring tolerance to toxic aromatic amine
3,4-dichloroaniline in soil[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, chemicals: Molecular and functional studies[J]. The Journal of
2008, 42: 8687-8691. Biological Chemistry, 2009, 284(28): 18726-18733.
[2] KUIPER J, HANSTVEIT A. Fate and effects of 3,4-dichloroaniline [18] BROOKE E W, DAVIES S G, MULVANEY A W, et al. An approach
(DCA) in marine plankton communities in experimental enclosures[J]. to identifying novel substrates of bacterial arylamine
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 1984, 8: 34-54. N-acetyltransferases[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2003,
[3] BREUGELMANS P, LEORY B, BERS K, et al. Proteomic study of 11: 1227-1234.
linuron and 3,4-dichloroaniline degradation by Variovorax sp. [19] CASTILLO J M, NOGALES R, ROMERO E. Biodegradation of
WDL1: Evidence for the involvement of an aniline dioxygenase- 3,4-dichloroaniline by fungal isolated from the preconditioning phase
related multicomponent protein[J]. Research in Microbiology, 2010, of winery wastes subjected to vermicomposting[J]. Journal of
161: 208-218. Hazardous Materials, 2014, 267: 119-127.
[4] VARJANI S, RAKHOLIYA P, NG H Y, et al. Microbial degradation [20] YAO X F, KHAN F, PANDEY R, et al. Degradation of
of dyes: An overview[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 314: 123728. dichloroaniline isomers by a newly isolated strain, Bacillus
[5] YUAN Y, ZHANG P, SCHMIDT B, et al. 3,4-Dichloroaniline revisited: megaterium IMT21[J]. Microbiology, 2011, 157: 721-726.